|
| Table 1 Rapid PACKTEST Results |
Showing posts with label Water Quality Monitoring Technique. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Water Quality Monitoring Technique. Show all posts
Sunday, 28 January 2018
Data Analysis of Rapid PACKTEST Results
January 28, 2018Learning Material, Mine Pollution, Mine Waste Management, Rapid PACKTEST, Water Quality Monitoring Technique
No comments

Upon the completion of the setup and PACKTEST, you have the data
available at hand to record. In your note book you record the readings of pH,
Turbidity, Temperature, metal conductivity. Then you have the other sets of
data from the PACKTEST results. Each element tested has got a numbered color
range that corresponds to the concentration of that element/compound in the
water sample. You record every data for the elements that are tested.
Be careful to graph the related data so that any conclusion drawn can
make sense with respect to particular information. i.e. if you plot all the
data into one graph then always take note of the legends so that your
interpretation is accurate in reporting.
It is also better to take readings at different weather patterns
i.e. during rainy seasons and dry seasons. Remember to keep the sample points
unchanged so that a good comparison is made.
From the data analysis, it is better to make few comments and off
course a recommendation is anticipated from the field investigation. Your
recommendation should provide a clear direction/ indication should there be precautions
taken within the vicinity of the impacted project area especially the mine
impacted communities. Your recommendation should also alert the local
government authorities regarding the findings and what to do in that part of the
area.
Tuesday, 16 January 2018
How to Conduct Rapid PACKTEST in a Well (below 1 meter in depth)
January 16, 2018Learning Material, Mine Waste Management, Mine Waste Treatment, Rapid PACKTEST, Water Quality Monitoring Technique
No comments

Well is simply a shaft sunk into the ground or built upwards from
certain depths below a natural surface of the ground which extends further
above certain heights of the natural surface of the ground
Wells can be naturally
occurring or man-made. Man-made wells are created to suite the desired
purpose(s) of the organisation or individuals. Wells can be created to collect water
or oil or gas below the earth’s surface.
In a mining operation, wells are created for the purposes of heap
leaching through a vat. Heap Leaching is one of the various mining techniques
to extract gold from the ore of various host rocks using cyanide which is one
of the common solvent in this gold recovery technique.
During the gold recovery process, cyanide is sprinkled over the
heap of crushed gold bearing gravels (ore) to dissolve the gold into a pregnant
solution or into liquid form. The pregnant solution is then sucked out through
the vat and further into carbon columns and take to the processing plant for
further processing and smelting.
Upon the closure of the mine, the vats are no longer in use. Cyanide
is left behind the pool beside the heap-vats eventually gets into the surrounding
environment which is a concern for mine waste management. Water is then filled
through the Vats up to certain heights. So
from the top and surface of the heap-vats, the water level is below certain depths
of about 2 – 3 meters which are hardly reached by hand. And also the diameter
of the vats is about 30-40 cm which is too narrow to be accessed. So how can
you how can you overcome this challenge to take a water sample for a Rapid PACKTEST
as well as other measurements?
The simple way to get sample is by utilizing the following
equipment procedures:
1. String line (rope)
2. Metal weight(1kg weight)
3. 3x1 Litre plastic bottle(container)
4. Masking tape
5. Water level measuring tape
6. GPS
7. Note book, pen, pencil
8. Camera
9. Blade/kitchen knife
11. Syringe
12. 0.45µm
filter
13. turbidity
meter
14. pH meter
15. Laptop/computer
Procedure
1. Cut the 1 Litre plastic bottles (container)
into more than half.
2. Tie the 1kg metal weight at the tip of the
string line.
3. With the masking tape, fasten the cut container
with the weight attached to the string line.
4. Drop the container attached to the weight
and stringline into the well and allow the container to be filled with water.
5. Pull the string line with all its attached
items and pour the fetched water into the other reserved containers.
6. Never forget to measure the water level by
using the 50m water level measuring tape.
7. Using the GPS you take the readings of
sample location coordinates and altitude and location zone.
8. Finally , you conduct Rapid PACKTEST and
9. Turbidity and pH measurements,
conductivity and temperature readings as well.
The above procedure can be repeated for wells or pools that are
hardly accessible in person or by hand.
Data Collection of the Rapid PACKTEST is the final thing to do before moving to the
next location or ending the field work.
Data Collection of Rapid PACKTEST Results
January 16, 2018Learning Material, Mine Pollution, Mine Waste Management, Rapid PACKTEST, Water Quality Monitoring Technique
2 comments

Data collection is the recording and assembling of results obtained from the Rapid PACKTEST experiments at various locations.
Before you conduct the packtests, you need to have the required materials for preparation, experiment and recording of data. The materials and equipment you would require for testing include but not limited to:
Packtest Kits.
GPS
Note Book
Pencil/pen
3 x Half cut container
syringe
0.45µm filter
Camera/smart phone with camera.
turbidity meter
pH meter
Laptop/computer
Once you have the above equipment list, you are about to conduct the PACKTEST and other necessary measurements. But before that you must never forget to give a sample location name or sample code/ID and record the coordinates, location zone and offcourse altitude of the sample location. This will ease the management of various data of the same type.
Thereafter, you proceed with the PACKTEST procedures as outline below which is a global practice:
Sampling Procedure for PACKTEST
1. Fetch water in container and filter the water using syringe and 0.45µm filter to filter water sample and pour filtered water sample into a clear mini cylinder(half cut container).
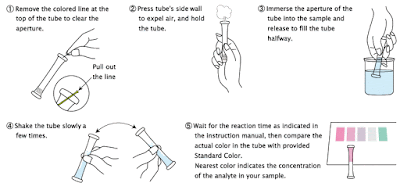
2. Remove the colored line at the top of the tube to clear the aperture.
3. Press tube's sidewall to expel air, and hold the tube.
4. Immerse the aperture of the tube into the water sample in the mini cylinder and release to fill the tube halfway.
5. Shake the tube slowly for few seconds.
6. Wait for the reaction time as indicated in the instruction manual, and then compare the actual color in the tube with provided Standard Color. The nearest color indicates the concentration value (mg/L = ppm) of the analyte in your sample.
Concurrently set up the equipment for measuring the pH, temperature, metal conductivity and turbidity of the water sample at the same sample location for the packtest water sample taken. After the setup is complete, you take the reading carefully as the reading varies every second. It is recommended to take the best average reading.
Upon the completion of the setup and PACKTESTs, you have the data available at hand to record. In your note book you record the readings of pH, Turbidity, Temperature, metal conductivity. Then you have the other sets of data from the PACKTEST results. Each element tested has got a numbered colour range that corresponds to the concentration of that element/compound in the water sample. You record every data for the elements that are tested.
Finally you need to digitise the data and analyse the test results. To do that, you need to have a computer or a laptop. Create an excel spread sheet in your laptop or computer and enter the field data in a tabulated format. Your sample results look like the table below:
How to do data analysis from the PACKTEST results and other measurements is in a different article (Data Analysis of Rapid PACKTEST Results)
Related Articles:
Rapid PACKTEST
Data Collection of Rapid PACKTEST Results
Data Analysis of Rapid PACKTEST Results
How to Conduct Rapid PACKTEST in a Well
Before you conduct the packtests, you need to have the required materials for preparation, experiment and recording of data. The materials and equipment you would require for testing include but not limited to:
Packtest Kits.
GPS
Note Book
Pencil/pen
3 x Half cut container
syringe
0.45µm filter
Camera/smart phone with camera.
turbidity meter
pH meter
Laptop/computer
Once you have the above equipment list, you are about to conduct the PACKTEST and other necessary measurements. But before that you must never forget to give a sample location name or sample code/ID and record the coordinates, location zone and offcourse altitude of the sample location. This will ease the management of various data of the same type.
Thereafter, you proceed with the PACKTEST procedures as outline below which is a global practice:
Sampling Procedure for PACKTEST
1. Fetch water in container and filter the water using syringe and 0.45µm filter to filter water sample and pour filtered water sample into a clear mini cylinder(half cut container).
2. Remove the colored line at the top of the tube to clear the aperture.
3. Press tube's sidewall to expel air, and hold the tube.
4. Immerse the aperture of the tube into the water sample in the mini cylinder and release to fill the tube halfway.
5. Shake the tube slowly for few seconds.
6. Wait for the reaction time as indicated in the instruction manual, and then compare the actual color in the tube with provided Standard Color. The nearest color indicates the concentration value (mg/L = ppm) of the analyte in your sample.
Concurrently set up the equipment for measuring the pH, temperature, metal conductivity and turbidity of the water sample at the same sample location for the packtest water sample taken. After the setup is complete, you take the reading carefully as the reading varies every second. It is recommended to take the best average reading.
Upon the completion of the setup and PACKTESTs, you have the data available at hand to record. In your note book you record the readings of pH, Turbidity, Temperature, metal conductivity. Then you have the other sets of data from the PACKTEST results. Each element tested has got a numbered colour range that corresponds to the concentration of that element/compound in the water sample. You record every data for the elements that are tested.
Finally you need to digitise the data and analyse the test results. To do that, you need to have a computer or a laptop. Create an excel spread sheet in your laptop or computer and enter the field data in a tabulated format. Your sample results look like the table below:
 |
| Table 1: Rapid PACKTEST Results |
Related Articles:
Rapid PACKTEST
Data Collection of Rapid PACKTEST Results
Data Analysis of Rapid PACKTEST Results
How to Conduct Rapid PACKTEST in a Well
Sunday, 24 December 2017
Rapid PACKTEST
December 24, 2017Learning Material, Mine Waste Management, Rapid PACKTEST, Training, Water Quality Monitoring Technique
No comments

Rapid PACKTEST is commonly known as PACKTEST. This test is a simple onsite method of testing water quality which produces amazing results in a split of a second. It does not require complicated analytical techniques to determine the quality of water. Concentration of heavy metals, precious metals and any other elements and compounds in the water are detected using this method. pH of water can also be determined using this method. Water in this case can be a flowing creek,settling ponds, pool beside vats or heap leach pads, mine pits etc.
 |
PACKTEST Results for Pihema Creek,
Morobe Province. Cyanide Detected
(Dark-blue).
|
It is recommended
that Pact Test should be practiced by all government regulators in the
extractive industries especially in the Mining and petroleum industry. This
will greatly help during statutory inspections which can give results instantly
onsite rather than waiting for results in the laboratory after few weeks or
months. This will also be a alert for the industry to treat waste water
effectively or improve on their waste water treatments and monitoring
techniques.
The process and the
setup of the testing method are outlined below.
Sampling Procedure for PACKTEST
1.
Fetch
water in container and filter the water using syringe and 0.45µm filter
to filter water sample and pour filtered water sample into a clear mini
cylinder.
2.
Remove the colored line at the top of the tube
to clear the aperture.
3.
Press
tube's sidewall to expel air, and hold the tube.
4.
Immerse
the aperture of the tube into the water sample in the mini cylinder and release
to fill the tube halfway.
5.
Shake
the tube slowly for few seconds.
6.
Wait
for the reaction time as indicated in the instruction manual, and then compare
the actual color in the tube with provided Standard Color. The nearest color
indicates the concentration value (mg/L = ppm) of the analyte in your sample.
Note: Cyanide is tested differently. Before the above procedure is applied,
first of all dissolve the mixing reagent into the filtered water in a small enclosed
translucent cube of about 2cm x 2cm x 1.5cm in size. Finally immerse the
cyanide reagent into the solution and release to fill up the tube. Shake the
tube and record the reading after 8 minutes.
The reaction times for
each element or compound varies from seconds to minutes. Reaction time for
cyanide takes longer than any other elements or compounds. It could be other
elements or compounds as well but during the tests conducted by the reporter
indicated that cyanide took longer than other elements.
It is recommended that
PACKTEST should be conducted on site. It would be a bad practice if sample is
taken from a different spot and date and tested on different date and location
as the results would not represent the sample location and time.
If you do then be aware to note the results and anticipate error in the
readings recorded.
Other Equipment for
testing water quality includes but not limited to pH meter, Turbidity Meter. pH
meter is for measuring the pH level of water
and also measure the temperature of water. Turbidity meter measures
turbidity of water and also temperature and metal conductivity in the water.
Tuesday, 27 June 2017
Relationship of pH and Conductivity of Heavy Metal Contents under Rainy Condition
pH increases as the conductivity is low in water. Heavy rain can increase the conductivity of heavy metals contents in water which reduce the pH of water.
During heavy rain you would expect a higher reading for conductivity and turbidity on the turbidity measuring equipment. at the same location and during dry days you would expect a different reading with low pH values.
During heavy rain you would expect a higher reading for conductivity and turbidity on the turbidity measuring equipment. at the same location and during dry days you would expect a different reading with low pH values.
Friday, 28 April 2017
Passive and Active Treatment of Mine Waste Water
April 28, 2017Learning Material, Mine Waste Management, Mine Waste Treatment, Water Quality Monitoring Technique
4 comments

 Active treatment is the water treatment in which continuous effort is required to improve the quality of water. It requires artificial ongoing energy inputs and bio-chemical or chemical reagents.
Active treatment is the water treatment in which continuous effort is required to improve the quality of water. It requires artificial ongoing energy inputs and bio-chemical or chemical reagents.Passive treatment is a intended water treatment method to improve the quality of water by the use of available natural materials or energy sources in the systems that minimises the regular maintenance for the system to operate effectively over the entire life of system design.
Benefits of Passive Treatment
- Reduces the cost of treatment
- Reduces labour cost - maintenance is almost free.
- Effective Natural purification
- Reduces operating cost (chemicals, electricity etc..)
- No disturbance to the natural landscape
Challenges of Active Treatment
- Capital and operational cost is very high.
- Requires more effort and close monitoring.
- Requires high cost of maintenance.
- Landscape disturbance is necessary.
Continuous research is required to develop a technology of how best and effective way that will minimise cost of installation and maintenance of active water treatment plants.