|
| Osarizawa Underground Mine Adit |
Showing posts with label Training. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Training. Show all posts
Saturday, 3 February 2018
Osarizawa Mine in Akita Prefecture, Japan
February 03, 2018Learning Material, Mining Regulators, Mining Technologies, Osarizawa Mine in Japan, Training
No comments

Osarizawa mine is an abandoned mine in Akita Prefecture,
Japan. Event though the mine is closed, the mine site is kept for sightseeing
purposes. The Osarizawa mine deposit is
a vein type deposit which was discovered in 708. The oldest Literature of
the mine was written in 1599 about the discovery of the Gojumaizawa gold
deposit which is part of the mine. The main commodities produced by the mine
were gold and copper.
The vein deposit was mined using the shrinkage stope mining method.
There are 15 levels and are 30m apart in height. The Total perimeter of the
mine levels is 700 km. The area of the mine site is 3km N-S by 2km E-W ~ 6km2 . Ceiling is 2-3m in
width.
The Level Zero starts at RL of about 300m and this is where the
access adit (ingress) is built. There are
5 levels above the zero level and 10
levels below zero level. The mining progressed upwards and mined materials were
collected at lower levels with the aid of gravity.
The host rock of the ore deposit is silicate mudstone which
is 10 times harder than concrete. Since the host rock is highly competent, the mine
was almost unsupported and less artificial support. Few supporting materials used
were logs/timbers of about 10mm to 300mm in diameter which were fitted well in between
mined out areas to prevent wall collapse. Other artificial supporting methods
are roof bolts, Mass wires and steel spiral cables drilled upwards to prevent
rocks from falling. Timbers are replaced every 10 years. The other supporting method used was the backfilling of
mined out areas with waste materials. Underground water is effectively under control
by plastic roofing gutters and drained out along the side of the concrete
pathway at each level.
The mined out ore/materials were transported by mini rail cars
which are powered by batteries. The rail cars were attached to one another like
train cars. The railways were built for these small battery powered rail cars. The
drilled or broken ores were loaded onto the rail cars and it required either
one or two operators to transport the materials out of the mine via shaft by
way of hoisting. At Zero Level the rail cars were driven out via the adit and
further to the processing plant for processing.
Production increased
with the increase in the rail cars.
Note:This article is an observation report and may not contain factual and detail information. The information here is kept at high level only. This article is subject to change if need be.
Sunday, 24 December 2017
Rapid PACKTEST
December 24, 2017Learning Material, Mine Waste Management, Rapid PACKTEST, Training, Water Quality Monitoring Technique
No comments

Rapid PACKTEST is commonly known as PACKTEST. This test is a simple onsite method of testing water quality which produces amazing results in a split of a second. It does not require complicated analytical techniques to determine the quality of water. Concentration of heavy metals, precious metals and any other elements and compounds in the water are detected using this method. pH of water can also be determined using this method. Water in this case can be a flowing creek,settling ponds, pool beside vats or heap leach pads, mine pits etc.
 |
PACKTEST Results for Pihema Creek,
Morobe Province. Cyanide Detected
(Dark-blue).
|
It is recommended
that Pact Test should be practiced by all government regulators in the
extractive industries especially in the Mining and petroleum industry. This
will greatly help during statutory inspections which can give results instantly
onsite rather than waiting for results in the laboratory after few weeks or
months. This will also be a alert for the industry to treat waste water
effectively or improve on their waste water treatments and monitoring
techniques.
The process and the
setup of the testing method are outlined below.
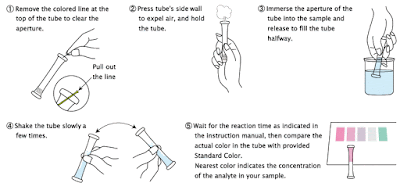
Sampling Procedure for PACKTEST
1.
Fetch
water in container and filter the water using syringe and 0.45µm filter
to filter water sample and pour filtered water sample into a clear mini
cylinder.
2.
Remove the colored line at the top of the tube
to clear the aperture.
3.
Press
tube's sidewall to expel air, and hold the tube.
4.
Immerse
the aperture of the tube into the water sample in the mini cylinder and release
to fill the tube halfway.
5.
Shake
the tube slowly for few seconds.
6.
Wait
for the reaction time as indicated in the instruction manual, and then compare
the actual color in the tube with provided Standard Color. The nearest color
indicates the concentration value (mg/L = ppm) of the analyte in your sample.
Note: Cyanide is tested differently. Before the above procedure is applied,
first of all dissolve the mixing reagent into the filtered water in a small enclosed
translucent cube of about 2cm x 2cm x 1.5cm in size. Finally immerse the
cyanide reagent into the solution and release to fill up the tube. Shake the
tube and record the reading after 8 minutes.
The reaction times for
each element or compound varies from seconds to minutes. Reaction time for
cyanide takes longer than any other elements or compounds. It could be other
elements or compounds as well but during the tests conducted by the reporter
indicated that cyanide took longer than other elements.
It is recommended that
PACKTEST should be conducted on site. It would be a bad practice if sample is
taken from a different spot and date and tested on different date and location
as the results would not represent the sample location and time.
If you do then be aware to note the results and anticipate error in the
readings recorded.
Other Equipment for
testing water quality includes but not limited to pH meter, Turbidity Meter. pH
meter is for measuring the pH level of water
and also measure the temperature of water. Turbidity meter measures
turbidity of water and also temperature and metal conductivity in the water.
Saturday, 17 June 2017
Mine Waste Management Training in Japan, 2017
Mine Waste Management Short training sponsored by Government of Japan through JICA in co-orporation with the Government of PNG through CEPA, MRA and DMPGM.
The training lasted two weeks and 6 officers from MRA and CEPA attended the training. The training comprise of theory and practicals and site inspections throughout Japan.
The training was a good exposure and skills acquired will be applied in drafting policies to encourage mining with environment friendly manner.This project will continue till 2018.
Monday, 1 May 2017
Mercury Pollution and Prevention Measures In Papua New Guinea
May 01, 2017Learning Material, Mine Pollution, Mine Waste Management, Mining Regulators, Safe Handling of Mercury, Training
No comments

Mercury is a heavy silvery-white liquid metal used in some thermometers and barometers. (Symbol: Hg). It is also used to extract fine gold from the mixture of fine sand. Dispose of mercury into the environment is harmful.
Mercury is used in many ways and people do not realize when it gets released into the environment which in turn causes mercury pollution.
In Papua New Guinea almost all Small Scale Miners use mercury in the amalgamation process during gold recovery from the fine sands. Mercury is used in different ways to recover gold. some pour in between the riffles on the sluice boxes in an attempt to capture fine-grained gold.
The contact time between the gold and mercury is not effective for the amalgamation to occur. Often fine gold remains suspended in the flow of particles above the riffles and does not settle to contact the mercury. Thus, about 30 percent (%) of the mercury used in sluice boxes in PNG is released into the river systems. This is actually a treat to the environment.
The Mineral Resources Authority's Small Scale Mining Branch in Wau- Morobe Province try its best to train local miners, especially small-scale miners, on the Safe Use and Handling Of Mercury in the process of amalgamation. The Training Center also trains the miners on other alternatives to be used in the gold recovery process to avoid the use of mercury.
Other alternative methods of gold recovery techniques the small scale miners should be looking at would be Gravity Separation methods in the recovery of fine gold.
Gravity separation methods are vital and the best alternatives to engaged instead of Mercury. Such methods include, but are not limited to:
Mercury is used in many ways and people do not realize when it gets released into the environment which in turn causes mercury pollution.
In Papua New Guinea almost all Small Scale Miners use mercury in the amalgamation process during gold recovery from the fine sands. Mercury is used in different ways to recover gold. some pour in between the riffles on the sluice boxes in an attempt to capture fine-grained gold.
The contact time between the gold and mercury is not effective for the amalgamation to occur. Often fine gold remains suspended in the flow of particles above the riffles and does not settle to contact the mercury. Thus, about 30 percent (%) of the mercury used in sluice boxes in PNG is released into the river systems. This is actually a treat to the environment.
The Mineral Resources Authority's Small Scale Mining Branch in Wau- Morobe Province try its best to train local miners, especially small-scale miners, on the Safe Use and Handling Of Mercury in the process of amalgamation. The Training Center also trains the miners on other alternatives to be used in the gold recovery process to avoid the use of mercury.
Other alternative methods of gold recovery techniques the small scale miners should be looking at would be Gravity Separation methods in the recovery of fine gold.
Gravity separation methods are vital and the best alternatives to engaged instead of Mercury. Such methods include, but are not limited to:
- Recovery of Fined Size of gold grain should use Shaking table, Humphreys spiral, Pinced sluices, Reichert cone, etc..
- Recovery of more finer gold particle should use Nelson concentrator, Falcon concentrator.
The mercury released into the environment is unaccounted for and undetected. Mercury can be detected by a Rapid Pack-test by use of Rapid pack test kits. However, rapid pack test is not available in the country and it is anticipated that pack-test kits will be imported from overseas to use for training and study purposes.
The next strategy is to ban import of mercury and introduce the alternative gold recovery methods and draft a treatment strategy through research and training.