1. Introduction
The Hidden Valley (HV) tailings dam/storage facility (TSF – Fig.1) is constructed with downstream method of embankment. The initial dam crest elevation was designed for RL 2,000 with a storage capacity of 40Mt of tailings with a mill throughput of 4.2Mtpa, (Rynhoud et al., 2017). The TSF has reached its designed capacity at RL 2,000 and the mining company plans to raise the dam height to RL 2,015 to increase the volume. In this study, it proposes for further 20m dam height expansion in two stages (RL 2,025 & RL 2,035) with the application of geotextile reinforcements for slope stabilization.
 |
| Fig.1 Hidden Valley (HV) tailings dam |
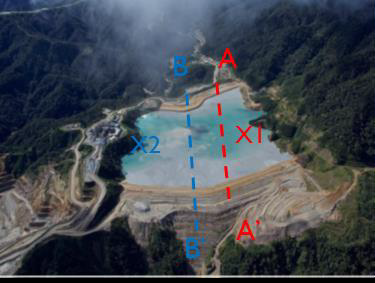
Analysis of the TSF is carried out in 2 cross sections (Fig.2) with 4 stages (stg): RL 2,000(stg.1), RL 2,015(stg.2), RL 2,025(stg.3), RL 2,035(stg.4). Phase2 software is used for numerical simulations with: (1) no reinforcement; (2) geotextile reinforcement. Desired critical shear strength reduction factor (SRF) is 1.3 and above.
 |
| Fig.2 Model view of section AA' and BB' at RL 2,000 |
3. Results, Discussion and Conclusion
 |
| Fig.3 Stability of dam at different RL with no support |



















